Unveiling the Power of Joint Attention in Learning

Key Highlights
- Joint attention is a critical skill for children's social and language development.
- Joint attention is the act of sharing an experience with someone through eye contact and shared focus.
- It helps children learn important skills like communication, turn-taking, and understanding emotions.
- Joint attention is supported by neurological foundations and plays a significant role in cognitive development.
- Parents and educators can use strategies and activities to foster joint attention in children.
Introduction

Joint attention is a fundamental skill that plays a crucial role in children's social and language development. It refers to the ability to share a common focus on an object or event with someone else through eye contact and shared attention. Joint attention skills enable children to engage in social interactions, communicate effectively, and understand others' perspectives.
For typically developing children, joint attention skills begin to develop as early as 6 to 9 months old. They start to exhibit behaviours such as looking towards a stuffed animal their parents are looking at or focusing on pictures in a book while sitting with a family member. These early experiences of joint attention lay the foundation for later language and social development.
In this blog, we will delve into the concept of joint attention in early learning, explore the science behind it, discuss strategies for parents and educators to foster joint attention, and highlight success stories and challenges in joint attention practices.
The Concept of Joint Attention in Early Learning
Joint attention is a critical concept in early learning that refers to the ability to share a common focus on an object or event with someone else. It involves using eye contact, gestures, and shared attention to communicate and connect with others. Joint attention skills are essential for social interaction, language development, and cognitive growth. By engaging in joint attention, children learn to take turns, understand others' perspectives, and develop important communication and social skills that lay the foundation for future learning and relationships.
Understanding the Basics of Joint Attention
At the core of joint attention is the ability to shift and share the focus of attention with another person. It requires a level of social cognition and an understanding of one's own and others' attention. For young children, joint attention involves following someone else's gaze or pointing gesture to an object of interest. It is a way of signalling to the other person to look at the same thing and share the experience. Joint attention also involves the child's ability to direct someone else's attention towards an object or event by using gestures, vocalizations, or eye contact. This back-and-forth communication through joint attention is crucial for developing social skills, language acquisition, and building strong connections with others.
The Role of Joint Attention in Cognitive Development
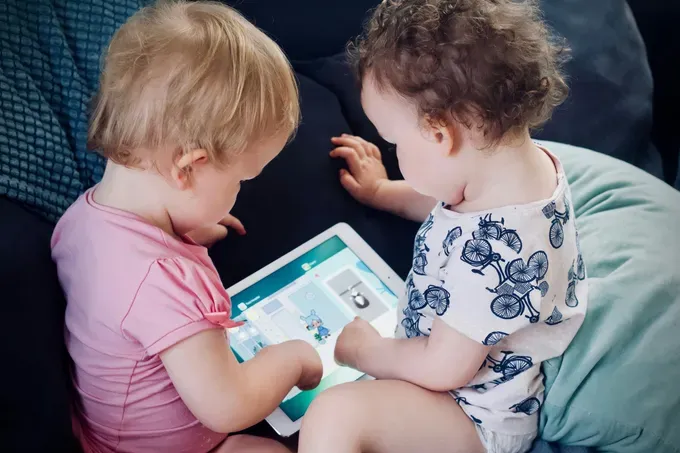

Joint attention plays a significant role in cognitive development, particularly in the areas of language skills and social understanding. Through joint attention, children learn to focus their attention on important elements in their environment and make connections between words and objects. This process supports language development and helps children understand the meaning behind words and gestures. Additionally, joint attention enhances children's ability to engage in reciprocal communication, express their thoughts and feelings, and develop problem-solving skills. It also fosters the development of social cognition, which is crucial for understanding others' thoughts, emotions, and intentions. Overall, joint attention is a vital building block for children's cognitive and language development, providing them with the necessary skills to navigate the social world and engage in meaningful interactions.
The Science Behind Joint Attention
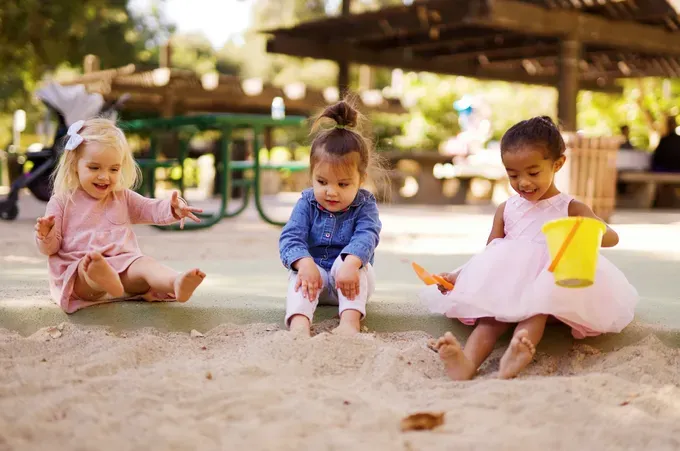

Understanding the science behind joint attention can shed light on its importance in early learning. Joint attention has been found to have strong neurological foundations, involving various brain regions responsible for social cognition. Studies have shown that joint attention skills are associated with language acquisition, as children who engage in joint attention tend to have better language skills. Visual attention, which is a component of joint attention, plays a crucial role in processing and perceiving the social cues that guide joint attention interactions. By unravelling the science behind joint attention, we can better appreciate its impact on children's learning and development.
Neurological Foundations of Joint Attention
The development of joint attention skills is supported by various brain regions that are involved in cognitive processes, social behaviour, and communication. These brain regions include the prefrontal cortex, the superior temporal sulcus, and the fusiform gyrus. The prefrontal cortex is responsible for executive functions such as attention, problem-solving, and decision-making, which are crucial for engaging in joint attention. The superior temporal sulcus plays a key role in processing social cues, such as eye contact and facial expressions, that are essential for successful joint attention interactions. The fusiform gyrus is involved in face recognition, enabling children to direct their attention towards others and establish joint attention. Understanding the neurological foundations of joint attention provides valuable insights into how this skill develops and its impact on cognitive development and social behaviour in children.
Joint Attention's Impact on Language Acquisition
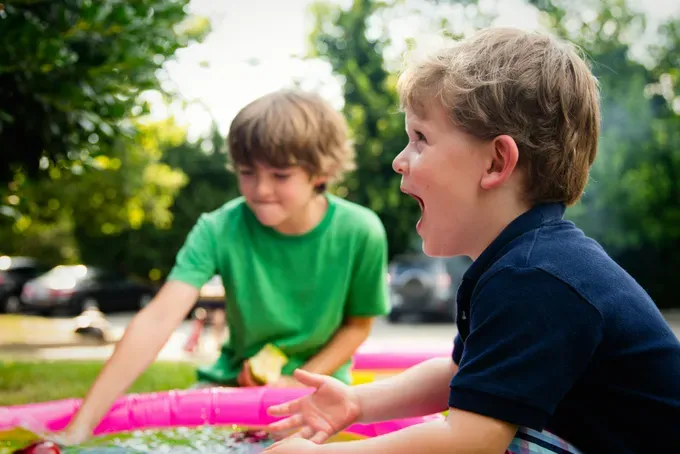

Joint attention has a significant impact on language acquisition in children. By engaging in joint attention interactions, children are exposed to rich language input and learn the meaning behind words and gestures. Joint attention enhances children's understanding of the social and communicative aspects of language, such as turn-taking, shared attention, and responding to others' communicative cues. This skill is particularly important for children with language difficulties who may benefit from speech therapy. Speech therapists often incorporate joint attention activities into their sessions to promote language development and improve communication skills. By fostering joint attention, children can enhance their language acquisition and develop the necessary skills to effectively communicate and engage in meaningful interactions with others.
Joint Attention Strategies for Parents and Educators
Parents and educators play a crucial role in fostering joint attention skills in children. By implementing joint attention strategies, they can create opportunities for children to engage in shared attention and develop their communication and social skills. Joint attention activities, such as reading books together, playing interactive games, and engaging in pretend play, provide rich contexts for joint attention interactions. These activities promote communication skills, social learning, and the development of strong connections between children and their caregivers or educators. By incorporating joint attention strategies into daily routines and educational settings, parents and educators can support children's learning and help them thrive both academically and socially.
Practical Ways to Foster Joint Attention at Home
Fostering joint attention at home can be done through simple yet effective strategies. Here are some practical ways to promote joint attention skills in children:
- Create opportunities for shared focus: Engage in activities that encourage joint attention, such as reading books, playing board games, or building puzzles together.
- Use facial expressions and gestures: Emphasize facial expressions and gestures while communicating with your child to enhance joint attention interactions. Use exaggerated facial expressions and hand movements to capture their attention and engage them in the shared experience.
- Incorporate joint attention into everyday life: Look for opportunities in everyday situations to practice joint attention skills. For example, point out objects of interest while taking a walk or involve your child in meal preparation by directing their attention to different ingredients.
- Follow your child's lead: Observe what activities and toys capture your child's attention the most and join in their play. This not only encourages joint attention but also promotes their autonomy and interests.
- Encourage turn-taking and reciprocal communication: Engage in back-and-forth interactions with your child, taking turns in activities and conversations. This helps develop their understanding of social cues and promotes joint attention skills.
By incorporating these practical strategies into daily routines, parents can create a supportive environment for the development of their child's joint attention skills.
Integrating Joint Attention in Educational Settings
Educators can play a vital role in promoting joint attention skills in educational settings. Here are some ways to integrate joint attention into the classroom:
- Plan activities that require shared attention: Design classroom activities that encourage children to engage in joint attention interactions, such as group projects or collaborative problem-solving tasks.
- Use visual aids and gestures: Incorporate visual aids and gestures into lessons to enhance joint attention. For example, use hand gestures or visual cues to direct children's attention to important information or prompts.
- Provide opportunities for turn-taking: Create opportunities for children to take turns and engage in reciprocal communication. Encourage active participation and sharing of ideas during group discussions or class presentations.
- Foster peer interactions: Create a supportive and inclusive classroom environment that promotes peer interactions. Encourage children to work together, share ideas, and engage in joint attention activities with their peers.
- Provide targeted support: Identify children who may need additional support in developing joint attention skills and provide targeted interventions or accommodations to meet their needs.
By integrating joint attention into educational settings, educators can enhance children's learning experiences, promote social interaction, and support their overall development.
Personalized Learning Through AI and Storytelling
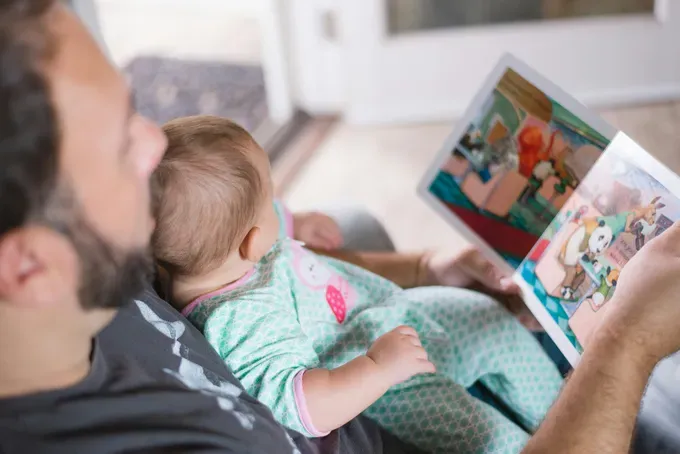

In recent years, personalized learning has gained prominence in education, and advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and storytelling, have revolutionized the way children learn. Personalized learning utilizes AI algorithms to tailor educational content to individual learners, taking into account their unique needs, interests, and learning styles. Storytelling, on the other hand, has long been recognized as a powerful tool for engaging children in the learning process and fostering their imagination and creativity. By combining personalized learning with storytelling and AI, educators can provide children with customized learning experiences that promote joint attention, enhance language acquisition, and support their overall development.
Enhancing Joint Attention with Personalized Books
Personalized books can be an effective tool for enhancing joint attention skills in children. These books are customized to include the child's name, interests, and experiences, making them highly engaging and relevant to the child's focus of attention. By immersing themselves in a personalized story, children are more likely to actively participate, maintain attention, and follow the narrative. This interactive and personalized approach to reading promotes joint attention, language learning, and the development of important cognitive and social skills. Through personalized books, children can explore new worlds, engage in shared experiences with their caregivers or educators, and foster a love for reading and learning.
The Future of Learning: AI's Role in Education
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform education by offering personalized learning experiences. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify individual learners' strengths, weaknesses, and learning preferences. By tailoring educational content to meet the unique needs of each learner, AI can enhance engagement, promote joint attention, and support the development of crucial cognitive and social skills. Additionally, AI can contribute to the understanding of individual differences in learning and help educators adapt their teaching strategies accordingly. Furthermore, AI can facilitate the development of theory of mind by providing learners with interactive and immersive experiences that foster empathy, perspective-taking, and understanding of others' thoughts and emotions. As AI continues to advance, its role in education holds great promise for creating inclusive, personalized, and effective learning environments.
Challenges and Solutions in Joint Attention Practices
While joint attention is a crucial skill, it is not without its challenges. Various factors can impact the development of joint attention skills in children. Some common barriers include difficulties with eye contact, attention, social referencing, and social skills. However, there are effective practices and solutions that can help address these challenges. By implementing strategies such as visual supports, structured routines, social stories, and individualized interventions, parents and educators can support children in overcoming these barriers and promoting the development of joint attention skills. Through collaboration, patience, and a strengths-based approach, the challenges associated with joint attention can be overcome, and children can thrive in their social and learning environments.
Common Barriers to Effective Joint Attention
Effective joint attention can be hindered by various barriers that children may face. Some common barriers include difficulties with social skills, eye contact, attention, and understanding social cues. Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder, for example, often struggle with joint attention due to challenges in social communication and interaction. These barriers can impact their ability to initiate and maintain shared attention with others. However, it is important to remember that these barriers can be addressed through targeted interventions, individualized support, and a nurturing environment that encourages social learning and communication. By acknowledging and addressing these common barriers, parents and educators can create opportunities for children to develop and enhance their joint attention skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, joint attention plays an invaluable role in children's cognitive and social development. By engaging in shared attention with others, children learn to communicate, understand different perspectives, and build meaningful relationships. Parents and educators can foster joint attention through various strategies, creating a supportive environment for children's learning and development. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as AI and personalized learning, offer exciting opportunities for enhancing joint attention and providing customized learning experiences. Despite the challenges, with the right support and interventions, every child can harness the power of joint attention to thrive in their social and learning environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is joint attention and why is it important?
Joint attention, also known as shared attention, is the shared focus of two individuals on an object or event. It is achieved when one individual alerts another to an object by means of eye-gazing, pointing, or other verbal or non-verbal indications. This involves one individual gazing at another, pointing to an object, and then returning their gaze to the individual to ensure mutual focus[1].
What age does joint attention develop?
Joint attention begins to develop as early as 6 to 9 months of age. During this period, infants start demonstrating behaviours such as following someone else's gaze or pointing gestures to an object of interest. These early experiences lay the foundation for later joint attention skills and social development.
How does joint attention benefit learning?
Joint attention benefits learning in various ways. It enhances language acquisition by providing children with meaningful contexts for understanding and using language. It also supports cognitive development and social skills, such as turn-taking and understanding others' perspectives. Overall, joint attention promotes positive learning outcomes and effective communication with others.
Citations:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joint_attention
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4258841/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3375497/
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.918181/full
https://web.uvic.ca/~dbub/Cognition_Action/Cog_Psych_Readings_files/Attention.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attention
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncom.2020.00029/full
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053810016303920
https://www.naset.org/fileadmin/user_upload/Autism_Series/Examples_IEP_Goals_Objectives_for_ASD.pdf
https://global.sacap.edu.za/blog/applied-psychology/types-of-attention/
https://www.jcs.mil/Portals/36/Documents/Library/Instructions/CJCSI 3500.01J.pdf
https://www.moore.army.mil/mssp/security topics/Potential Adversaries/content/pdf/JP 3-0.pdf
https://virtualspeech.com/blog/active-listening-skills-examples-and-exercises
https://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/definition/english/joint_2
https://therapiesforkids.com.au/blog/pointing-for-children-5-18-months/
https://www.verywellhealth.com/adhd-stimming-5208900
https://www.iasplus.com/en/standards/ifrs/ifrs11
https://www.aihr.com/blog/knowledge-skills-abilities-ksa-examples/
Written By AI